Introduction
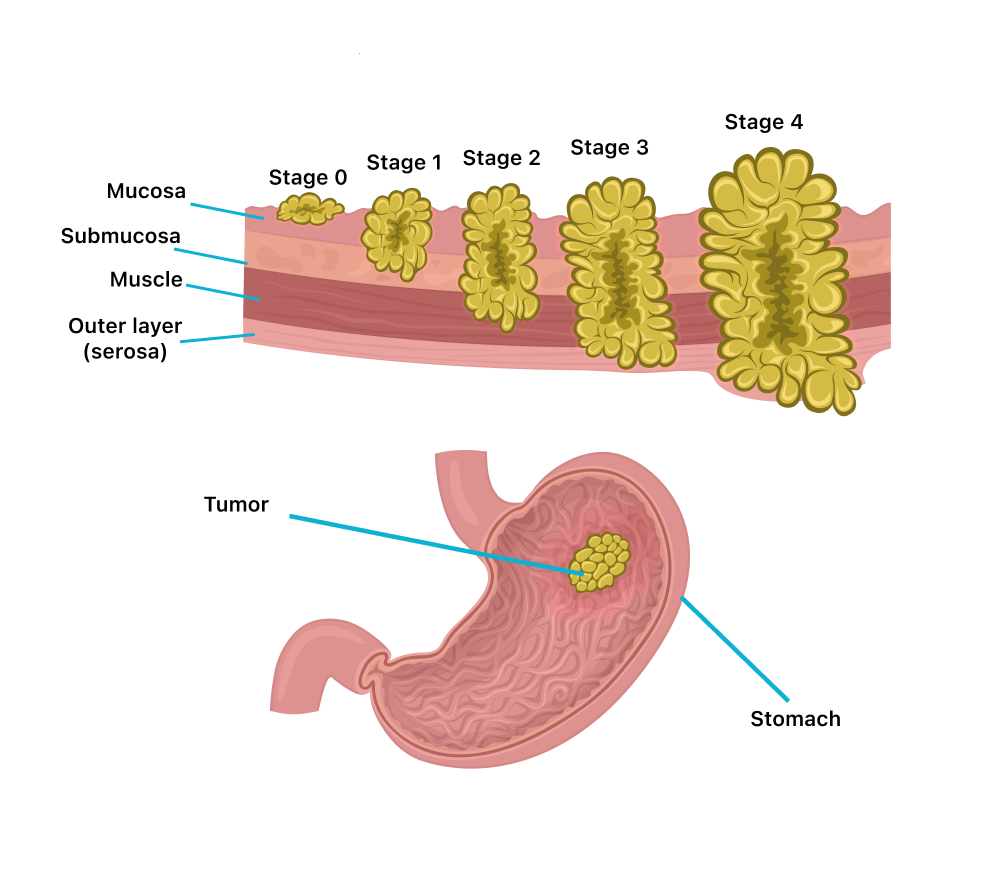
Stomach cancer starts mostly either in the stomach body or the esophagus. Before the actual cancer even starts, the inner-linings of the stomach change, which usually doesn't cause any symptoms. The types of stomach cancer include adenocarcinomas (most common and forms in the innerlining of the stomach), gastrointestinal stromal tumors (froms in stomach wall, sometimes in other part of difestive tract), Neuroendocrine tumors (form in digestive tract), and lymphomas (forms in lymphocytes, sometimes in stomach). Many things can cause stomach cancer, including disease, a person's actions, and hereditary reasons (more detailed)
Mechanisms and genetic alterations
The most common mutated genes for stomach cancer are TP53, LRP1B, ARID1A, PIK3CA, CIC, ERBB4. The most common copy number alteration genes are MYC, CDKN2A, CCNE1.
Current stomach cancer treatments
The preferred treatment is surgery, but chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted drugs are also used. At the early stages of stomach cancer, surgery is used to often remove either part of the stomach or the whole thing, with nearby lymph nodes getting removed as well. At the stage where the cancer has grown more in the stomach but hasn't spread too far through the body, a scan will be used to find out if surgery or chemotherapy/radiaton therapy is used initially. If surgery is done, then sometimes chemo is done to make sure all the cancer is gone. If chemo or radiation therapy is used first, then surgery is used after the cancer has shrunk. If the stomach cancer hasn't gone far through the body but is too large for surgery to get rid of it all, then a combination or selection of chemo, immunotherapy, targeted drugs, or radiation therapy is used. After this surgery is used if the cancer has gotton smaller. If not, then there is more treatment done to prevent further spread of the cancer and limiting the effects it has on the patient. Once the cancer has grown far throughout the body, the previously stated treatment is done with the focus being on limiting the spread of the cancer and limiting the effects of it on the patient.
New treatments in clinical trials